Young, Black, Healthcare Heroes Are Tackling Disparities During Dueling Pandemics
Wearing an N-95 mask, a full-body yellow gown, and latex gloves, Rebecca Hamilton, a newly registered nurse, was ready for her fourth shift on the medical surgery floor at a local South Florida hospital. Full of nerves and grateful for the opportunities afforded to her, Rebecca's career as a Black registered nurse is beginning at a time when the United States is encountering the dueling pandemics of COVID-19 and racial injustice.
Like so many others entering professions in healthcare, Rebecca is treating patients during a pandemic which has disproportionately claimed the lives of Black, Brown and vulnerable citizens, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
"I finished my nursing education during a global pandemic. I took my nursing board exam during a global pandemic, and now I'm treating patients on the frontline of the COVID-19 pandemic," said Rebecca Hamilton, a South Florida native. "My first priority is learning how to best serve my patients in this direst of circumstances — especially when far too many of them look like me."
Hamilton's path to the healthcare industry started with a spark from her late grandmother. As a first-generation American family with Jamaican roots, Hamilton says her family rallied around her grandmother day and night, especially during the illness which caused her death. During that period, Hamilton then a high school student, was responsible for taking her grandmother to doctor's appointments and follow-up visits, and filling prescriptions. This journey as an end-of-life caregiver gave the future registered nurse a front-row seat to see the disparities and changes needed within the healthcare industry for people of color.
"As my grandmother's illnesses compounded, I saw the healthcare industry from a new set of eyes, those of the Black elderly. With doctors' appointments stacking up one after another, I realized that my grandmother didn't understand what was happening to her. The healthcare professionals in charge of care never took the time out to explain things in a meaningful way. She was left alone in a healthcare system all by herself, and it wasn't right,” said Hamilton.
This life experience and mentoring from the many Jamaican-trained registered nurses in Hamilton’s tight-knit church community, inspired her shift from an undecided major at Florida Atlantic University to a nursing student at Broward College. "I was lucky that I started my training before COVID-19 and got a chance to get some real hospital experience before the pandemic hit," she said. “Now, I work in a hospital that treats COVID patients and those with COVID results pending. I think about the health and well-being of parents at home and those in my community who have succumbed to this pandemic due to preexisting chronic illnesses."
With her grandmother's praying hand ring on one of her ring finger, Hamilton continues to learn the ropes for a high-demand career filled with opportunity. "The COVID-19 pandemic has given a voice to nurses and healthcare workers like me,” Hamilton said. “In school, we learned about nursing. As a healthcare professional, I'm learning about nursing during a pandemic," she continued. "Nursing and the healthcare industry overall can be difficult and overwhelming at times, but I feel like there are so many opportunities to grow, learn and better serve my community,” she said.
Hamilton enters the field amid a nursing shortage and at a time when the Black registered nursing education pipeline has been severely curtailed, a situation likely ensuring less diverse healthcare workforces in the future, to the detriment of Black patients and families.
Health disparities are a continual problem in the United States. According to Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity at The George Washington University, people of color experience poorer outcomes and shorter life expectancy than their white counterparts. The underrepresentation of Black, Brown, and Indigenous people in many healthcare professions — including those requiring an advanced degree — contributes to these health gaps.
"COVID-19 has made health disparities more evident," said Edward Salsberg, a researcher for the Mullan Institute of Health Workforce Equity. "Having a diverse healthcare workforce is a key component to solving these disparities and ensuring quality healthcare for Black patients, especially with regards to patient communications, preventative care, and patient satisfaction."
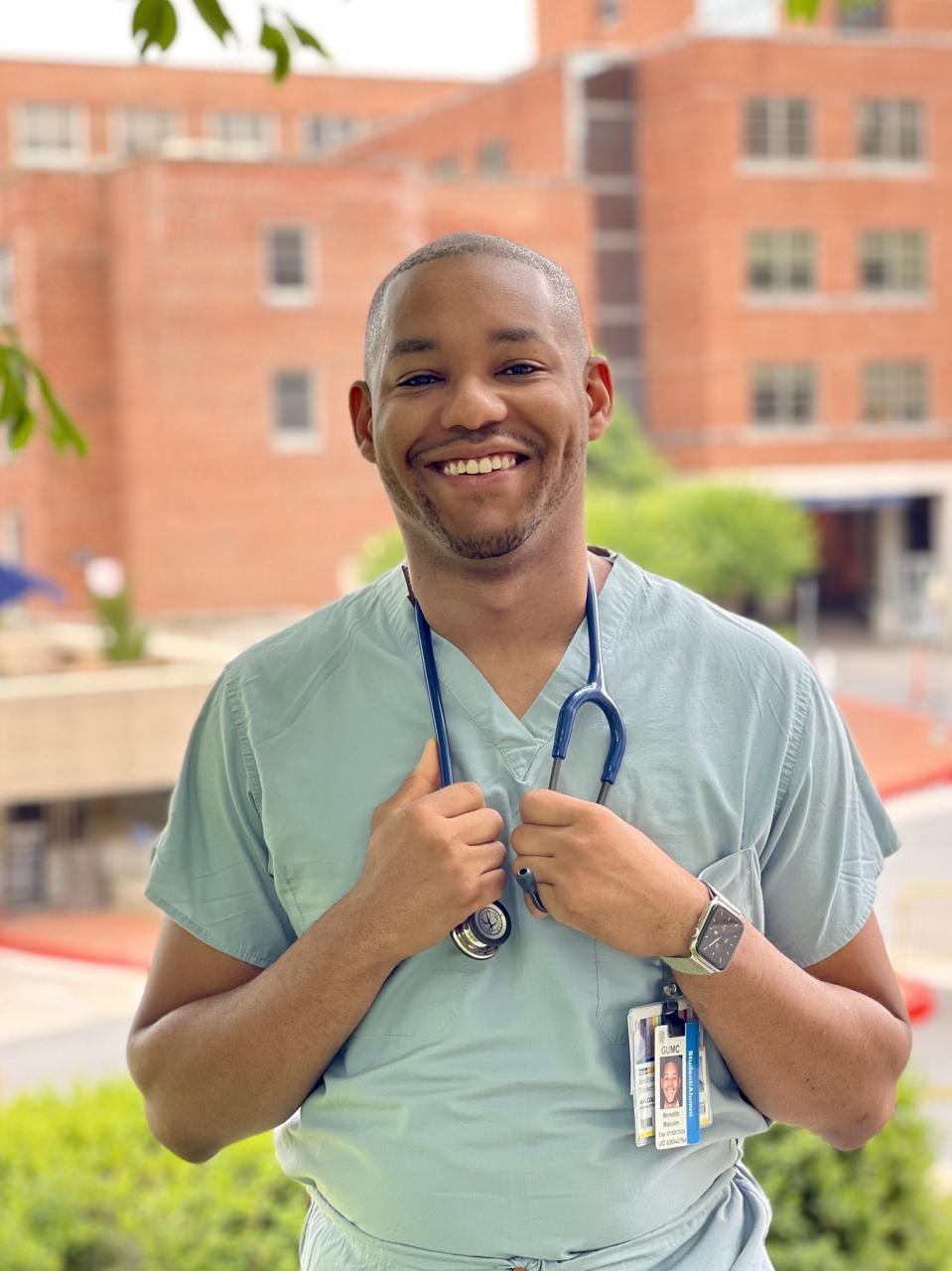

Malcolm Meredith, a third year medical students, pictured outside of the Medstar Georgetown ... [+]
RICHARD FOWLER
These disparities are just one reason Georgetown University School of Medicine's third-year clinical student Malcolm Meredith decided to become a physician. As one of two Black men in his class of more than 200 students, Meredith currently serves as the Student Executive Council president for the Georgetown School of Medicine — a role held by just a few people of color in the school's 170 years of existence.
"At one point in time, someone that looked like me couldn't attend the school I attend. Women couldn't attend the school I attend. And, poor folks couldn't attend the school I attend," said Meredith. "We have made some amazing strides since those days, but we still have a lot of work to do. As a clinical student, you can actually see the difference in how patients respond when they see someone that looks like them at the bedside, even if my knowledge is still limited,” he said.
Georgetown University's School of Medicine has been vocal about racial injustice in America. It has taken an active role to work collaboratively with its student body on issues of diversity and inclusion.
Meredith, also a graduate of Morehouse College and native of LeGrange, Georgia, has had a passion for healthcare since he was a child. Like Hamilton, he was also guided into medicine after watching his grandmother struggle with a chronic healthcare condition.
"I am going into healthcare, medicine in particular, because I have witnessed first-hand the difference a caring doctor can make in someone's life. Not just in their health, but also in their everyday quality of life," Meredith said. "There is something so fulfilling about using your knowledge of science and medicine to help people live better quality lives,” he said.
While most medical students find their journey to be challenging, those who are Black have more significant socioeconomic challenges on top of the emotional and academic demands. These challenges have only been made worse by the COVID-19 pandemic and the rise of racial injustice.
"Accepting more Black medical students into a program is not enough. To ensure that we have an increase in the number of Black physicians, schools need to work with their current students and help them overcome obstacles while in medical school," said Meredith. "During my experience as a student, I yearned for guidance on balancing my identities of being both Black and a physician-in-training. I have had trouble getting it. And I know my story isn't unique amongst Black med students at this school or other predominantly white institutions,” he said.
Meredith, interested in entering a surgery specialty upon completing medical school, believes the best way to encourage more Black students to enter professions in healthcare is by addressing the issues beyond admissions making the road difficult. Some of those issues he says are: a lack of mentoring programs, insufficient financial assistance, and the need for better awareness of diversity and inclusion throughout the medical education process.
"As a clinician student and leader on my campus, I want my pathway and story to be an example and beacon of optimism of what is possible," Meredith said. "What has come out of [the] COVID-19 pandemic is more people being committed to doing something, and I hope that younger Black folks will join me in the healthcare profession so we can help the underserved in our community,” he said.
It looks like Meredith’s hopes are becoming a reality. According to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), 2020 saw a 10.5 percent increase in Black first-year medical students, and a 12.2 percent increase among Black men enrolling in their first year of medical school. 2020 also saw an estimated 18 to 20 percent increase in the number of Black, Brown, and Indigenous applicants to M.D. granting institutions.
These are all signs that Norma Poll-Hunter Ph.D., AAMC's senior director of workforce diversity, called promising. "We see an increase of Black, Brown and Indigenous applicants applying for medical schools [throughout] the United States and in Puerto Rico," she said. "There is also a greater concentration of pipeline and pre-medical programs aimed at eliminating many of the barriers these students face when they decide to pursue a career in medicine,” said Poll-Hunter. "The role that Black physicians play in the healthcare workforce cannot be understated. They are more likely to locate their practices in underserved communities. They are more likely to serve patients and families on Medicaid. And most importantly, they are more likely to increase healthcare outcomes for people of color,” she said.
Improving healthcare outcomes will require breaking down the lingering distrust in the healthcare industry by the Black community. With that mistrust at an all time high, adding more Black professionals in the healthcare industry might be key to putting Black patients at ease. "There is a lot of mistrust in our healthcare system, especially amongst people of color, '' said Poll-Hunter. "This mistrust can only be broken down if more Black people get into the field of patient care and at the decision-making table,” she said.
Both Rebecca Hamilton and Malcolm Meredith are shining examples of young Black people answering the call to serve their community in the healthcare profession.
As the COVID-19 pandemic seemingly comes to an end, the racial injustice pandemic continues. With healthcare workers still standing on the frontlines, the question remains of whether the representation and lived experience of Black physicians, nurses, physician assistants, respiratory therapists, advanced practice registered nurses, and other healthcare professionals be valued.
 Attendees
Attendees
 Sponsors and Exhibitors
Sponsors and Exhibitors
 AI In Healthcare: A Virtual Course
AI In Healthcare: A Virtual Course
 Contact us
Contact us